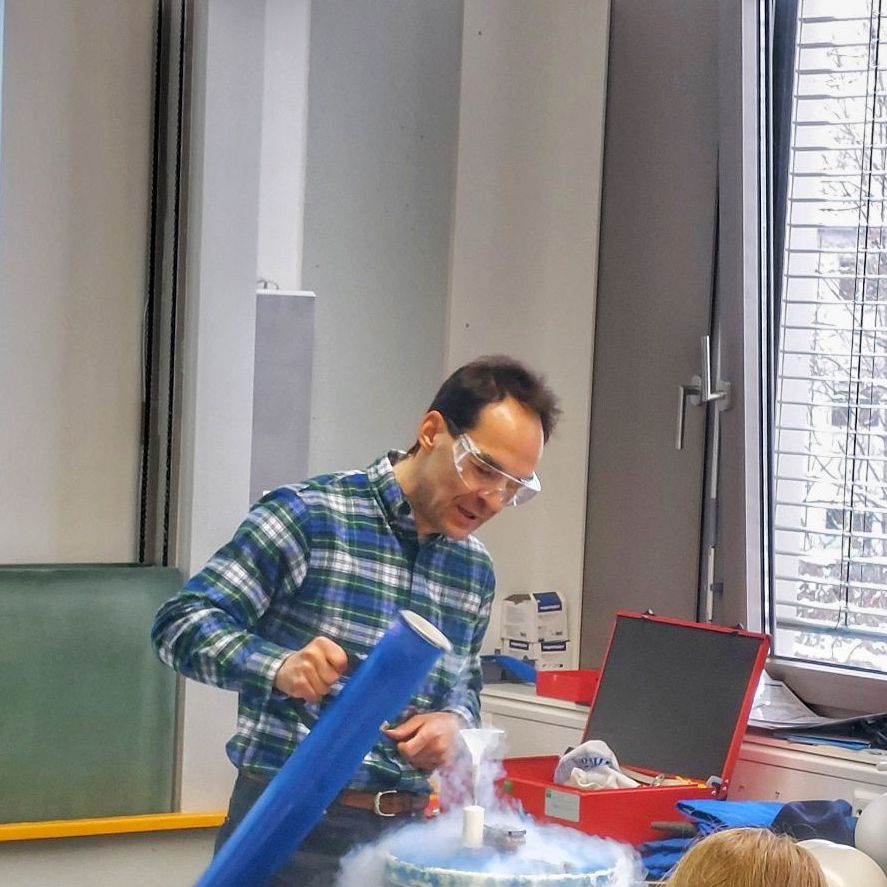
Matthias Opel hosted 9 physics teachers from the Michaeli-Gymnasium in Munich. They performed experiments at low temperatures with liquid nitrogen. Matthias explained the Meißner-Ochsenfeld effect and showed the levitation of a high-Tc (YBa2Cu3O7−δ) superconductor above a permanent magnet by demonstrating the superconducting WMI racetrack. Achim Marx and Matthias Opel then took them on a tour in the institute and showed the quantum physics and the spintronics labs. Finally, Matthias explained how magnetic fields influence the electrical resistivity of materials, known as "magnetoresistance effect".
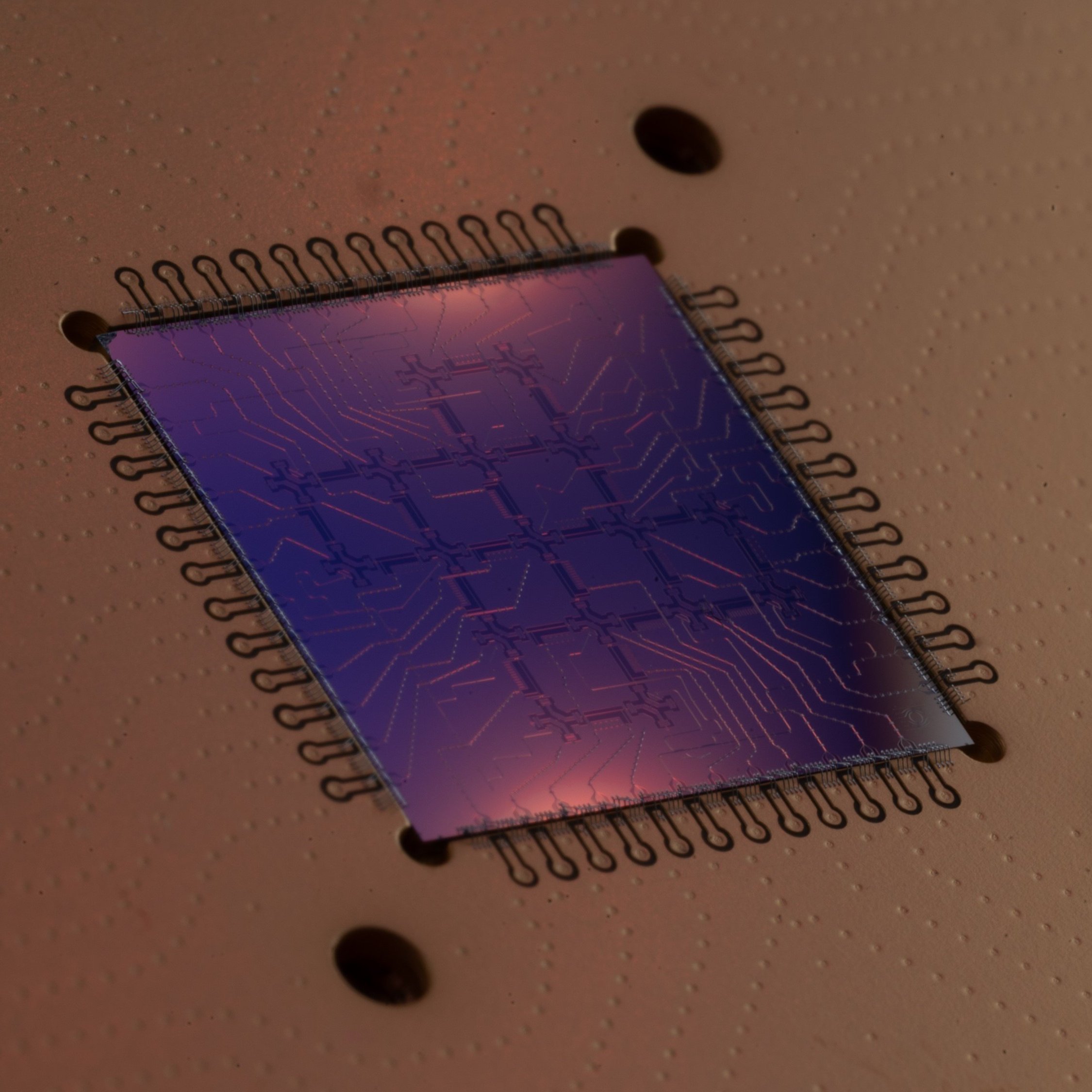
The latest publication of the quantum computing group at WMI (published in Rev. Phys. Appl.) was featured in "Physics" as an editor's pick. Researchers at WMI have demonstrated that replacing aluminum with niobium for on-chip air bridges can significantly improve the robustness of superconducting quantum processors. Beyond their usual role in routing, the team integrated these air bridges directly as capacitive elements in superconducting qubits and achieved median coherence times of 51.6 µs. A promising step toward more resilient and scalable quantum devices!
This work was supported by Munich Quantum Valley, MUNIQC-SC, the Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology, and the OpenSuperQPlus Flagship project.
The European Union has awarded €25 million to the SUPREME consortium. The project brings together 23 European companies and research organisations (including WMI) to fabricate and demonstrate a 3D-integrated quantum computer with 200 qubits.
Over the next 3.5 years, SUPREME will showcase improved stability, higher yield, and greater reproducibility in the key fabrication processes for superconducting quantum chips - an important step toward industrial-scale quantum technologies.
Read the full press release here.
We look forward to achieving this ambitious goal together with all our partners.
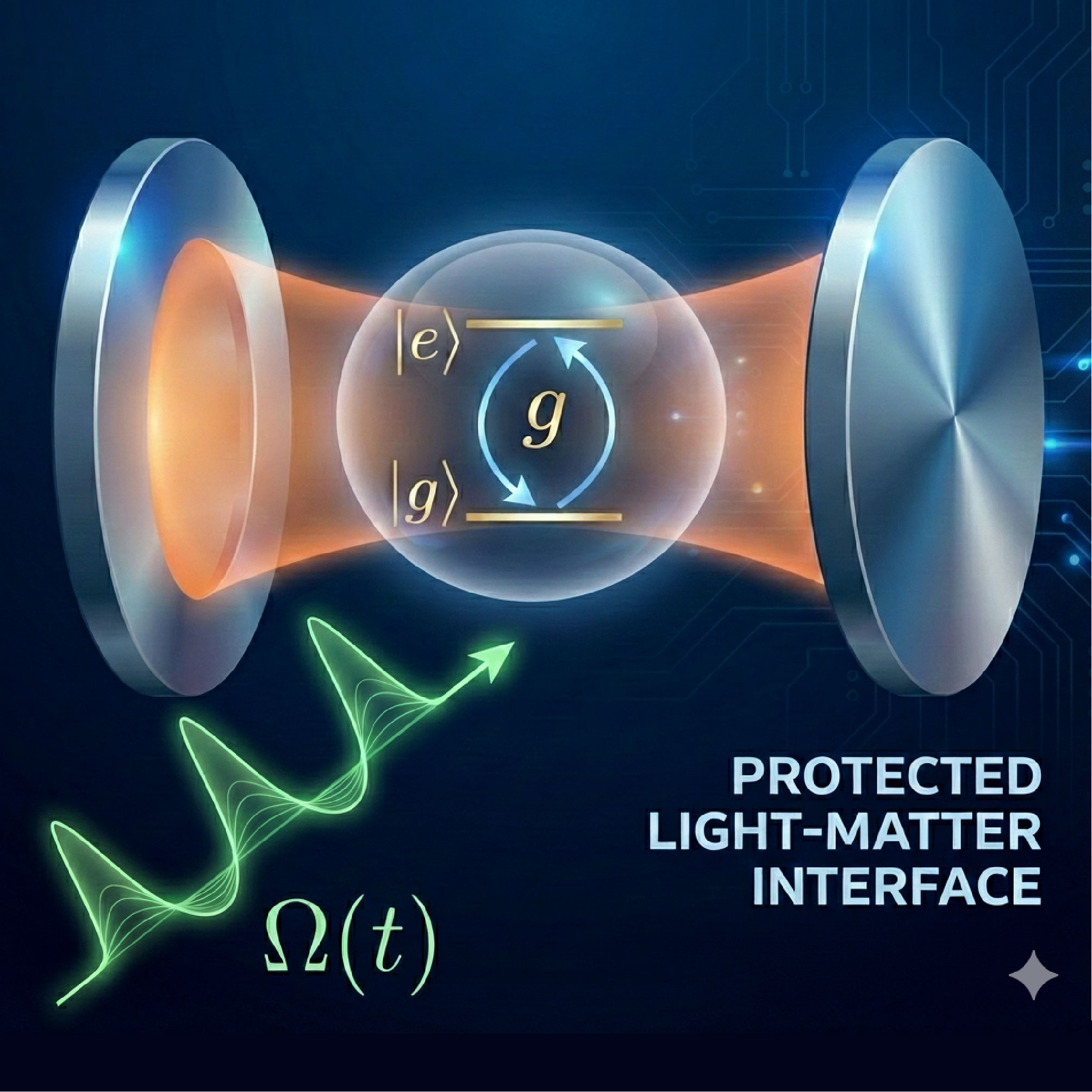
In an idle stage, quantum information stored in stationary qubits can be protected against ubiquitous low-frequency noise by periodically flipping the 0 and 1 states with a sequence of fast control pulses—a technique known as 'spin echo.' So far, however, such techniques have not been applicable while a qubit is coupled to a microwave or optical mode, which is necessary to mediate long-range gate operations and to implement quantum communication protocols. In an international collaboration with researchers from Bilbao, Paris, and ETH Zurich, the theory group at WMI has now developed a new control strategy that closes this gap and enables the protection of quantum states during their interaction with a photonic mode. This technique is completely general and can be applied to a wide range of quantum technological applications that rely on coherent interfaces between qubits and photons.

TUM President Thomas Hofmann presented the certificate of appointment as TUM Emeritus of Excellence to Rudolf Gross at the general meeting of the TUM Senior Excellence Faculty (SEF) on 1 December 2025. Since 2007, the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has honored outstanding and dedicated retired professors with the honorary title of TUM Emerita/Emeritus of Excellence (EoE) and involves them in the university's work on a voluntary basis. The TUM Emeriti of Excellence are considered valuable advisors due to their personal independence, extensive experience, and high academic reputation. The interdisciplinary group of TUM Emeriti of Excellence forms the TUM Senior Excellence Faculty (SEF).

Since 2000, the State Ministry of Science and the Arts has been awarding the PRO MERITIS SCIENTIAE ET LITTERARUM prize to outstanding individuals for their services to science and the arts. On October 28, 2025, Minister of State Blume presented this award to Rudolf Gross, the long-standing director of WMI. "He laid the foundations for the institute's international leadership position. With his deep technical expertise and strategic foresight, he has made the Bavarian quantum ecosystem what it is today – one of Europe's most important centers for quantum research – through the first Collaborative Research Center on solid-state-based quantum information processing, the two clusters of excellence NIM and MCQST, and the Munich Quantum Valley", Minister Blume emphasized.